Approved Fuel-System Hose Clamps: Don’t Leave Home Without Them


Hose clamps make sure hoses stay put and prevent potentially deadly fuel leaks, but not everyone understands how they need to be used on an NMMA-certified boat. ABYC standards are very specific around the fuel system, as they should be. Take a look at the standards for gasoline and diesel systems here.

Boat Building Standards:
Hose Clamps for Fuel Systems
ABYC Standards--
Hose Clamps on Gasoline Fuel Systems
EXCEPTIONS:
1. Clamps used with outboard engine primer bulb assembly(s).
2. Clamps used in connections of fuel hose from the primer bulb to the outboard engine(s)
-
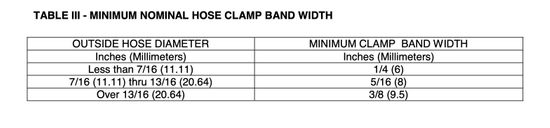
Hose connections used in the fuel tank vent system or the fuel distribution and return line system shall have at least one corrosion resistant metallic clamp with a minimum nominal band width (see table below).
-
All components of hose clamps shall have a resistance to corrosion equal to or greater than 300 series stainless steel.
-
Hose clamps shall be reusable.
-
Flexible hose not equipped with permanently attached end fittings, such as swaged sleeve and threaded insert, shall be attached with corrosion resistant metallic clamps. NOTE: Some USCG Type A hose is not designed to be clamped.
-
Hose shall not be installed on helical threading or knurling that provides a path for fuel leakage.
-
Clamps depending solely on the spring tension of the metal shall not be used.
-
Clamps shall be installed to impinge directly on the hose, and shall not overlap each other.
-
Clamps shall be beyond the flare or bead, or fully on serrations where provided, and at least 1/4 inch (6.35 mm) from the end of the hose.
-
Hose used in the fuel tank fill system shall be secured to pipes (smooth pipes acceptable), spuds or other fittings at each connection, by at least two corrosion resistant metallic clamps with nominal band widths of at least 1/2 inch (12.7 mm).
Hose Clamps on Diesel Fuel Systems
NOTE: Some USCG Type A hose is not designed to be clamped.
-
Flexible hose shall be equipped with permanently installed end fittings, such as a swaged sleeve or a sleeve and threaded insert, or may be secured with corrosion resistant metallic clamps.
-
Flexible hose not equipped with permanently attached end fittings, such as swaged sleeve and threaded insert, shall be attached with corrosion resistant metallic clamps.
-
Clamps depending solely on the spring tension of the metal shall not be used.

-
Clamps shall be installed to impinge directly on the hose and shall not overlap each other.
-
Clamps shall be beyond the flare or bead, or fully on serrations where provided, and at least 1/4" (6 mm) from the end of the hose.
-
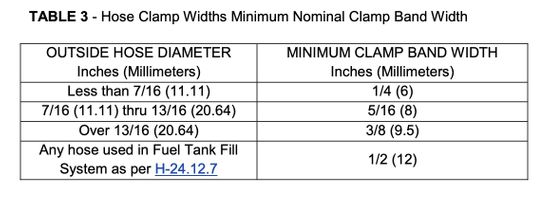
Hose used in the fuel tank fill system shall be secured to pipes (smooth pipes acceptable), spuds or other fittings at each connection, by at least two corrosion resistant metallic clamps with nominal band widths of at least 0.5" (12 mm).
-
Hose connections used in the fuel tank vent system or the fuel distribution and return line system shall have at least one corrosion-resistant metallic clamp with a minimum nominal band width as indicated in the table below.
-
All components of hose clamps shall have a resistance to corrosion equal to or greater than 300 series stainless-steel.
-
Hose clamps shall be reusable.
-
Hose clamps shall be corrosion resistant metallic clamps with nominal band widths of at least 0.5" (12 mm)